What is the GMAT?
The GMAT or Graduate Management Admissions Test is an aptitude test for applicants to Masters of Business Administration programs. It is not an IQ test but simply a measure of your performance on standardized tests.
The GMAT Exam Structure
As of 2019, you may choose which order you wish to take the exam in.
- Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA)
- Integrated Reasoning
- Multiple-Choice
- Verbal Reasoning
- Quantitative Reasoning
Analytical Writing Assessment
- Time Limit: 30 minutes
- # of Questions: 1 question
- Question Types: Analysis of an Argument
- Score Range: 0-6 (in 0.5 point increments)
In this section, you must develop an essay. The essay calls on you to critique the position of the author in the argument presented. You will compose this essay on the computer screen.
Integrated Reasoning
- Time Limit: 30 minutes
- # of Questions: 12 questions
- Question Types: Graphics Interpretation, Table Analysis, Multi-Source Reasoning, Two-part Analysis
- Score Range: 1-8 (in 1 point increments)
In this section, you will be asked to evaluate information from various sources. The questions are a mix of verbal and quantitative challenges.
Multiple-Choice
Verbal Reasoning
- Time Limit: 65 minutes
- # of Questions: 36 questions
- Question Types: Reading Comprehension, Critical Reasoning, Sentence Correction
- Score Range: 6-51 (in 1 point increments)
Quantitative Reasoning
- Time Limit: 62 minutes
- # of Questions: 31 question
- Question Types: Data Sufficiency, Problem Solving
- Score Range: 6-51 (in 1 point increments)
GMAT Computer Adaptive Testing
The Quantitative and Verbal Reasoning sections of the GMAT are computer-adaptive. According to MBA.com, “the first question you receive will be of medium difficulty.
If you answer the first question correctly, the computer will usually give you a harder question. If you answer the first question incorrectly, your next question will be easier. This process continues until you complete the section, using responses to all previously answered questions, at which point the computer will have and accurate assessment of your ability in that subject.
You will not be able to skip, return to, or change your answers to questions. This is because the computer uses your response to each question to select the next one.”
How is the GMAT scored?
The GMAT has three separate scores for each section.
Analytical Writing Assessment
- holistically scored 0-6
- .5 point increments
Integrated Reasoning
- 1-8
- 1 point incremenets
- must answer each part correctly to get credit for the question
- not included in Overall score
Multiple Choice
- 0-60
- 1 point increments
- a two-digit number
- the sectional subscore
Overall Score
- subscores combined
- three-digit number
- 200-800
- average score is approximately 550
- scores on separate sections do not affect each other
What does the GMAT test look like?
The GMAT starts out with an untimed tutorial which teaches the basics of how to naviaget the test on the computer. Once you complete the tutorial, you will move into the next section of the test in the order that you have chosen.
Each section begins with timed instructions for the questions you are about to see. If you have studied the types of questions, you will not need to spend time reading these. You can save time and go ahead with your test.
GMAT Strategy for Adaptive Testing
As stated in the section above, the GMAT uses adaptive testing. According to Crash Course for the GMAT 4th Edition, as you take the test, “the computer revises its assessment of you, both by giving you questions that are more or less difficult (depending on your answers), and by adjusting its estimate of your score up and down, until has enough information to assign you a subscore for that section. Your subscores are then simply added and converted to your composite score.”
Because of this style of adaptive testing, this means that earlier questions in the test are more important to get correct than later questions. You should spend more of your time making sure that you get the first questions correctly, as getting later questions wrong won’t affect your score as much if you have already answered many of the early questions correctly. Try to spend no more than three minutes on any one question.
Techniques for taking the GMAT
Process of Elimination
While reading through the answer choices for each question, you should identify which answers are wrong in order to leave you with the correct answer and a higher probability of choosing the correct answer.
Watch the Clock
Make sure to answer every question in the section by keeping an eye on the clock. If you fail to answer every question, you will be penalized in your score. The computer takes the score calculated up to that point and reduces it by the percentage of the test unfinished.
Use Your Noteboards
You will receive a booklet of noteboards to use as scratch paper. Noteboards are laminated card stock in the size of legal paper with a graph paper grid.
Get into the habit of writing down each question with the choices A, B, C, D, E on your noteboard. Cross out each answer as you eliminate it. Once you come to your answer, you can circle or underline the correct answer to stay organized.
Integrated Reasoning Is Not Adaptive
The Integrated Reasoning section of the test is linear, and the questions do not get harder as you answer them correctly. The pacing for a linear section is different than for an adaptive section.
Pacing Guidelines
- Do the easiest parts of each question first.
- Guess and move on if you are stuck on a question for too long.
Integrated Reasoning Scores
- Scoring is all or nothing. You must answer all questions correctly in each part to get points for the part.
- Some questions are experimental and do not count towards your score. These questions are only there for the test-makers to evaluate.
The Calculator
The on-screen calculator is available for the Integrated Reasoning section but not for the Quantitative section. You will have to perform calculations by hand for the Quantitate section.
- MC – memory clear key – use this key to clear any values stored in the memory
- MR – memory recall key – use this key to recall the value you have stored using the memory store key
- MS – memory store key – use this key to store the number currently on the screen
- M+ – memory addition key – use this key to add the onscreen number to the value in the memory
- Backspace – clear the last digit entered
- CE – clear entry button – use this button to correct a mistake on a longer calculation without starting over
- C – clear key – use this key to start a calculation over
- sqrt – square root key – click this key after entering the number you want to take a square root of
- % – use this key to take a percentage without entering a decimal
- 1 /x – click this key after entering the number you want to take the reciprocal of
GMAT Question Types
Table Analysis

- Sort By drop-down box: different ways to sort the data in the table
- Standard directions for a Table Analysis question: no need to re-read for each question
- Additional directions: tailored to the question with further specific information, not necessarily needed to be re-read for each question
- Information explaining the table: recapped information about the table
- Questions: You can not leave any parts blank.
Study the column headings first and then go to the statements to save time.
Graphics Interpretation

- The chart, graph or image: could be scatter plot, bar chart, line graph, or circle
- Explanation of the graph or chart: what the chart represents and additional information about the measurements
- Questions: must answer all questions to move on, usually a drop-down box in the middle of a sentence with 3-5 answer choices
Two-Part Analysis
This section’s questions are similar to conventional math word problems with two variables. You need to pick an answer for each variable that makes some condition true.

- The actual problem: the description of two variables, the condition that needs to be made true. Read carefully.
- Description of how to pick your answers: text varies slightly from problem to problem
- Answer choices: generally five or six answer choices, choose one for each column, possible that the same number is the answer for both columns
Most Two-Part Analysis questions use simple arithmetic. However, there are also Critical Reasoning questions interlaced.
Multi-Source Reasoning
These questions present information on tabs. It can be text, charts, graphs or a combination.
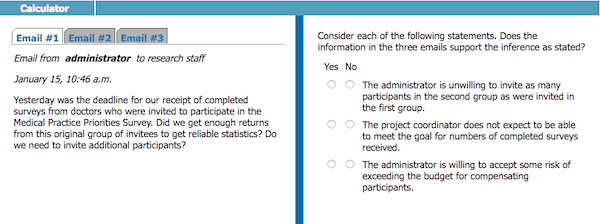
- Tabs across the top left of screen: some indication of what’s on the tab, could be graphs, tables, charts, or text, be sure to check out each tab before answering questions
- Information for each tab: with graphs, check out the axes and look for a legend or other information to explain; with tables, check out the column headings; read all headings
- Basic instructions for responding: explain how you need to evaluate each statement, determine whether statements are valid inferences, evaluate statements for true or false
- Actual questions: pick a response for each statement or you won’t be able to advance to the next question
These questions usually come in sets with three separate questions with two usually in the statement style. You may also get multiple-choice questions with five answer choices as part of a set.
Don’t forget to look on all tabs and get familiar with the information before responding to questions.
Next Article >> Ten Steps to the GMAT | Sentence Corrections
Sources: Crash Course for the GMAT 4th Edition, MBA.com
